本文主要讲解Spring源码中经常看到的类的作用,中间会有会有部分代码讲解,各模块的具体源码会写在后面的文章中
BeanDefinition BeanDefinition中保存了我们Bean的信息。声名式bean的定义下面三种方式 xml配置spring 在读取bean配置信息后会给bean配置生成对应的BeanDefinition象对象存储类信息供spring生产bean使用。我们也可以直接使用beanDefinition生成一个bean。
public static void main (String[] args) AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition().getBeanDefinition(); beanDefinition.setBeanClass(People.class ) ; applicationContext.registerBeanDefinition("myBean" ,beanDefinition); applicationContext.refresh(); System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean(People.class )) ; System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("myBean" )); }
BeanDefinitionReader 顾名思义,这个类的作用就是读取类配置。它主有很多实现类,例如XmlBeanDefinitionReader 读取的就是方式配置
XmlBeanDefinitionReader <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-autowire ="byName" > <bean id ="people" class ="spring.bean.People" /> </beans >
public static void main (String[] args) AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(applicationContext); int i = beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions("applicationContext.xml" ); System.out.println(i); }
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 注意:这个类并不是解析被@Bean,@Component注解修饰等类,而是解析需要加载的类的一些配置信息如:@Scope,@Lazy
@Scope ("prototype" )public class People }
public static void main (String[] args) AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(applicationContext); beanDefinitionReader.registerBean(People.class ) ; applicationContext.refresh(); System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("people" )); System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("people" )); }
*People.class设置它的作用范围为原型。从结果上面可看出两次得到的People对象确实是不同的
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 通过包扫描注解解析@Component(@Bean注解不会bei扫描)
package spring.bean;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component public class People }
public static void main (String[] args) AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner classPathBeanDefinitionScanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(applicationContext); classPathBeanDefinitionScanner.scan("spring.bean" ); applicationContext.refresh(); System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean(People.class )) ; }
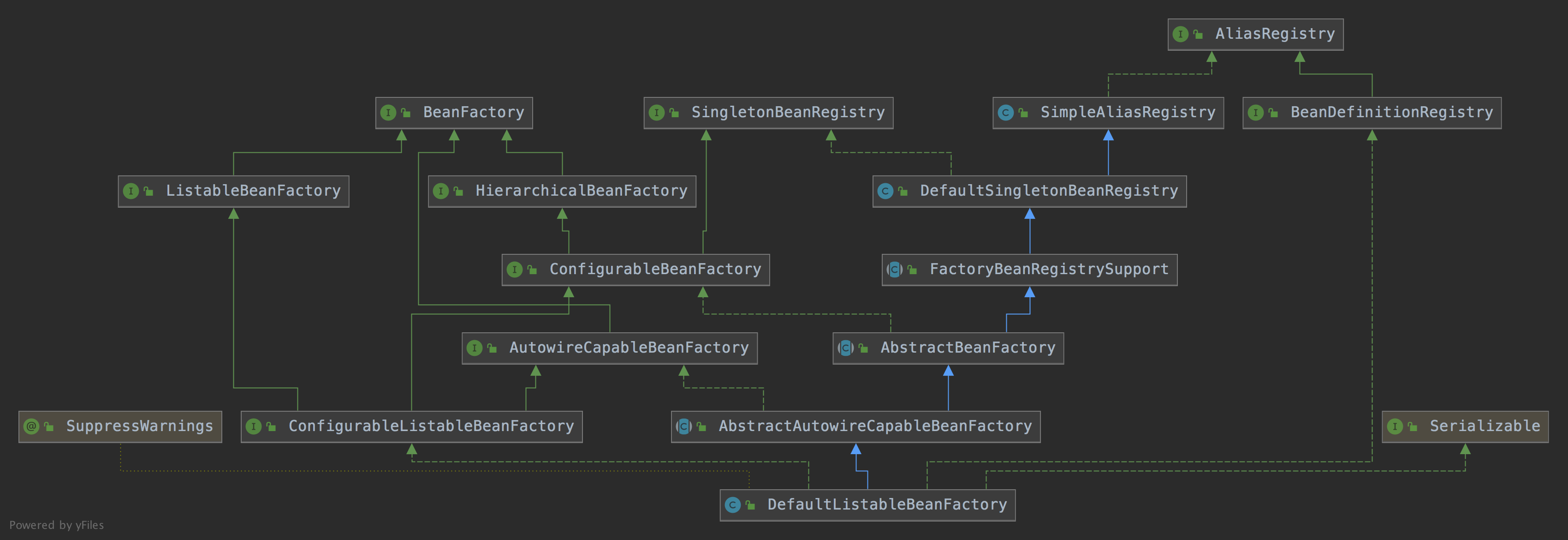
BeanFactory Spring中有很多种BeanFactory,本文以它中比较核心的实现类DefaultListableBeanFactory讲解 DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了很多接口表示拥有很多功能
AliasRegistry:支持别名功能,一个名字可以对应多个别名
BeanDefinitionRegistry: 可以注册、保存、移除、获取某个BeanDefinition
BeanFactory:可以根据bean的名字、类型、别名获取Bean对象
SingletonBeanRegistry: 可以直接注册、获取单例bean
SimpleAliasRegistry:它是一个类,实现了AliasRegistry接口中所定义的功能,支持别名功能
ListableBeanFactory:在BeanFactory的基础上,增加了其他功能,可以获取所有BeanDefinition的beanNames,可以根据某个类型获取对应的beanNames,可以根据某个类型获取{类型:对应的Bean}的映射关系
HierarchicalBeanFactory:在BeanFactory的基础上,添加了获取父BeanFactory的功能
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry:它是一个类,实现了SingletonBeanRegistry接口,拥有了直接注册、获取某个单例Bean的功能
ConfigurableBeanFactory:在HierarchicalBeanFactory和SingletonBeanRegistry的基础上,添加了设置父BeanFactory、类加载器(表示可以指定某个类加载器进行类的加载)、设置Spring EL表达式解析器(表示该BeanFactory可以解析EL表达式)、设置类型转化服务(表示该BeanFactory可以进行类型转化)、可以添加BeanPostProcessor(表示该BeanFactory支持Bean的后置处理器),可以合并BeanDefinition,可以销毁某个Bean等等功能
FactoryBeanRegistrySupport:支持了FactoryBean的功能
AutowireCapableBeanFactory:是直接继承了BeanFactory,在BeanFactory的基础上,支持在创建Bean的过程中能对Bean进行自动装配
AbstractBeanFactory:实现了ConfigurableBeanFactory接口,继承了FactoryBeanRegistrySupport,这个BeanFactory的功能已经很全面了,但是不能自动装配和获取beanNames
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory:继承了ListableBeanFactory、AutowireCapableBeanFactory、ConfigurableBeanFactory
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory:继承了AbstractBeanFactory,实现了AutowireCapableBeanFactory,拥有了自动装配的功能
DefaultListableBeanFactory:继承了AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,实现了ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口和BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,所以DefaultListableBeanFactory的功能很强大
通过以上分析,我们可以知道,通过DefaultListableBeanFactory我们可以做很多事情
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition().getBeanDefinition(); beanDefinition.setBeanClass(People.class ) ; DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("people" , beanDefinition); beanFactory.registerAlias("people" , "people1" ); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LubanBeanPostProcessor()); System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean("people1" )); System.out.println(beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(People.class )) ;
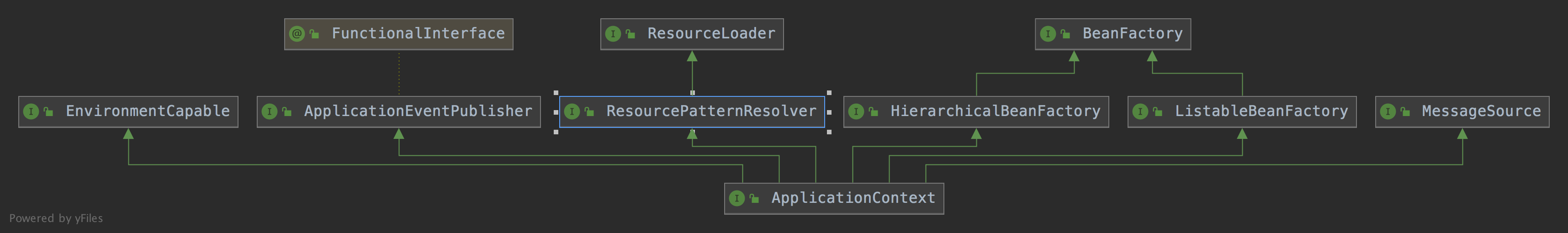
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext是一个接口,可以把它理解成一个特殊的BeanFactory
HierarchicalBeanFactory:拥有获取父BeanFactory的功能
ListableBeanFactory:拥有获取beanNames的功能
ResourcePatternResolver:资源加载器,可以一次性获取多个资源(文件资源等等)
EnvironmentCapable:可以获取运行时环境(没有设置运行时环境功能)
ApplicationEventPublisher:拥有广播事件的功能(没有添加事件监听器的功能)
MessageSource:拥有国际化功能
下面用两个比较重要的实现类进行讲解
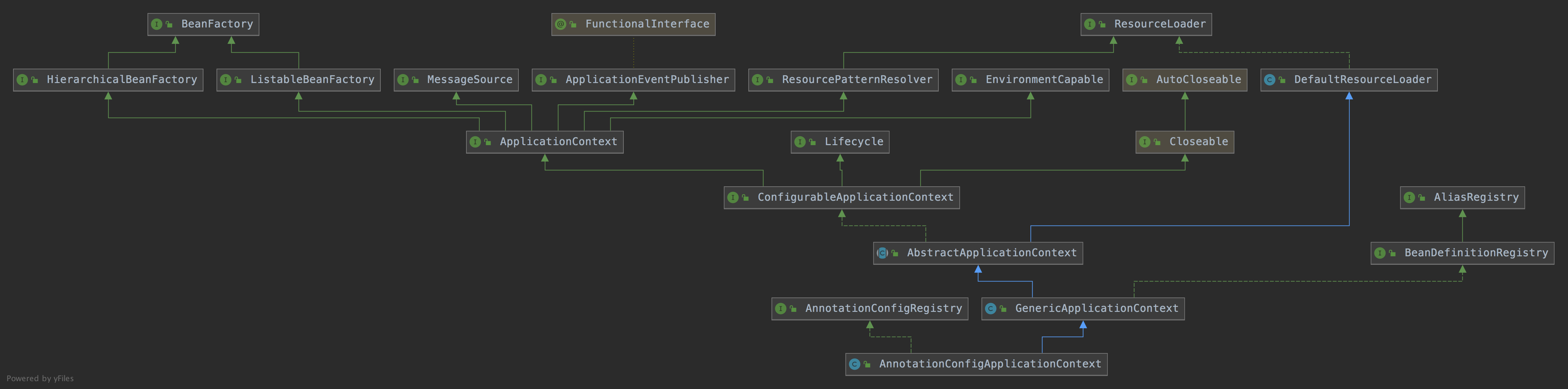
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
ConfigurableApplicationContext:继承了ApplicationContext接口,增加了,添加事件监听器、添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor、设置Environment,获取ConfigurableListableBeanFactory等功能。
AbstractApplicationContext:实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口
GenericApplicationContext:继承了AbstractApplicationContext,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,拥有了所有ApplicationContext的功能,并且可以注册BeanDefinition,注意这个类中有一个属性(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
AnnotationConfigRegistry:可以单独注册某个为类为BeanDefinition(可以处理该类上的@Configuration注解,处理@Bean注解),同时可以扫描。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:继承了GenericApplicationContext,实现了AnnotationConfigRegistry接口,拥有了以上所有的功能。
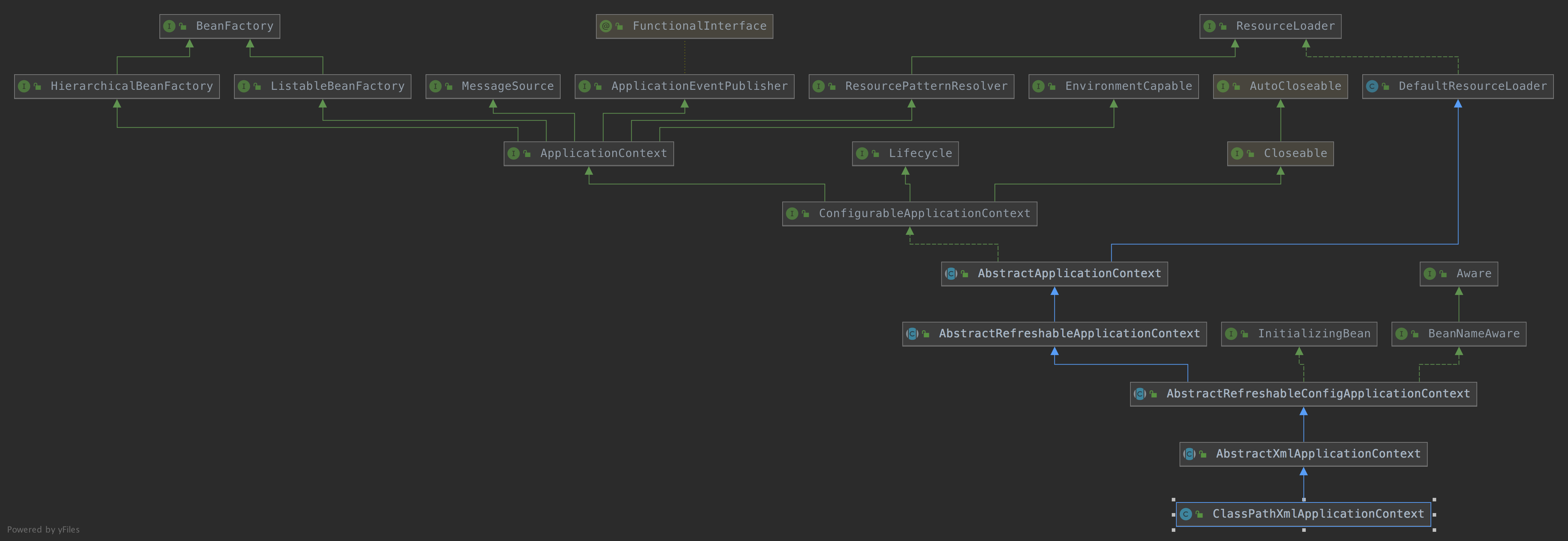
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 它也是继承了AbstractApplicationContext,但是相对于AnnotationConfigApplicationContext而言,功能没有AnnotationConfigApplicationContext强大,比如不能注册BeanDefinition
国际化 定义一个MessageSource
@Bean public MessageSource messageSource () ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); messageSource.setBasename("messages" ); return messageSource; }
使用
annotationConfigApplicationContext.getMessage("test" , null , new Locale("en_CN" ))
资源加载 ApplicationContext还拥有资源加载的功能,比如,可以直接利用ApplicationContext获取某个文件的内容
Resource resource = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getResource("file://D:\\IdeaProjects\\spring-framework\\zzf\\src\\main\\java\\com\\zzf\\entity\\People.java" ); System.out.println(resource.contentLength());
classpath获取
Resource resource = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getResource("classpath:com/zzf/entity/People.class" ); System.out.println(resource.contentLength());
一次性获取多个
Resource[] resources = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getResources("classpath:com/zzf/service/*.class" ); for (Resource resource : resources) { System.out.println(resource.contentLength()); }
获取运行时环境 annotationConfigApplicationContext.getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment(); annotationConfigApplicationContext.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties(); annotationConfigApplicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("xxx" )
事件发布 定义一个事件监听器
@Bean public ApplicationListener applicationListener () return new ApplicationListener() { @Override public void onApplicationEvent (ApplicationEvent event) System.out.println("接收到了一个事件" ); } }; } annotationConfigApplicationContext.publishEvent("事件XXX" );
发布事件
类型转化 PropertyEditor JDK中提供的类型转化工具类
public class StringToPeoplePropertyEditor extends PropertyEditorSupport implements PropertyEditor @Override public void setAsText (String text) throws IllegalArgumentException People people = new People(); people.setName(text); this .setValue(people); } }
StringToPeoplePropertyEditor propertyEditor = new StringToPeoplePropertyEditor(); propertyEditor.setAsText("1" ); People value = (People) propertyEditor.getValue(); System.out.println(value);
Spring中注册PropertyEditor
@Bean public CustomEditorConfigurer customEditorConfigurer () CustomEditorConfigurer customEditorConfigurer = new CustomEditorConfigurer(); Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> propertyEditorMap = new HashMap<>(); propertyEditorMap.put(People.class , StringToPeoplePropertyEditor .class ) ; customEditorConfigurer.setCustomEditors(propertyEditorMap); return customEditorConfigurer; }
@Component public class PeopleService @Value ("true" ) People test; public void test () System.out.println(test); } }
ConversionService Spring中提供的类型转化服务,它比PropertyEditor更强大
public class StringToPeopleConverter implements ConditionalGenericConverter @Override public boolean matches (TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) return sourceType.getType().equals(String.class ) && targetType .getType ().equals (People .class ) ; } @Override public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes () return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(String.class , People .class )) ; } @Override public Object convert (Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) People people = new People(); people.setName((String)source); return people; } }
DefaultConversionService conversionService = new DefaultConversionService(); conversionService.addConverter(new StringToPeopleConverter()); People value = conversionService.convert("1" , People.class ) ; System.out.println(value);
Spring 中注入ConversionService
@Bean public ConversionServiceFactoryBean conversionService () ConversionServiceFactoryBean conversionServiceFactoryBean = new ConversionServiceFactoryBean(); conversionServiceFactoryBean.setConverters(Collections.singleton(new StringToPeopleConverter())); return conversionServiceFactoryBean; }
TypeConverter 整合了PropertyEditor和ConversionService的功能,Spring内部使用
SimpleTypeConverter typeConverter = new SimpleTypeConverter(); typeConverter.registerCustomEditor(People.class , new StringToPeoplePropertyEditor ()) ; People value = typeConverter.convertIfNecessary("1" , People.class ) ; System.out.println(value);
BeanPostProcessor Bean的后置处理器,可以在创建每个Bean的过程中进行干涉,是属于BeanFactory中一个属性,Bean的生命周期文章中详细讲。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor Bean工厂的后置处理器,是属于ApplicationContext中的一个属性,是ApplicationContext在实例化一个BeanFactory后,可以利用BeanFactoryPostProcessor继续处理BeanFactory。 程序员可以通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor间接的设置BeanFactory,比如上文中的CustomEditorConfigurer就是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,我们可以通过它向BeanFactory中添加自定义的PropertyEditor。
FactoryBean 允许程序员自定义一个对象通过FactoryBean间接的放到Spring容器中成为一个Bean。 那么它和@Bean的区别是什么?因为@Bean也可以自定义一个对象,让这个对象成为一个Bean。 区别在于利用FactoryBean可以更加强大,因为你通过定义一个XxFactoryBean的类,可以再去实现Spring中的其他接口,比如如果你实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,那么你可以在你的XxFactoryBean中获取到Bean工厂,从而使用Bean工厂做更多你想做的,而@Bean则不行。