Spring容器 什么是容器 官网解释
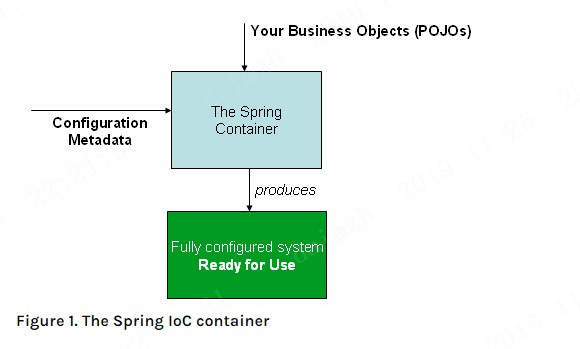
The org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext interface represents the Spring IoC container and is responsible for instantiating, configuring, and assembling the beans.
翻译内容:
总结:
代码层面:Spring容器是实现了ApplicationContext接口的对象。
功能层面:Spring容器是Spring框架的核心,作用是管理对象。容器会创建对象,连接对象,并管理它们整个生命周期(创建到销毁).
容器如何工作
Spring容器通过我们提交的POJO对象以及配置元数据产生一个充分配置的可以使用的系统。这里说的配置元数据,实际上我们就是我们提供的XML配置文件,或者通过注解方式提供的一些配置信息
Spring Bean 实例化bean 构造器创建 1.无参构造器
<bean name="people" class "com.zzf.entity.People" > </bean>
2.有参构造器标签指定构造器参数值,其中index表示位置,value表示常量值,也可以指定引用,指定引用使用ref来引用另一个Bean定义.
<bean name="people2" class "com.zzf.entity.People" > <constructor-arg index="0" value="zzf"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" value="18"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="2" ref="collection"></constructor-arg> </bean>
静态工厂方法创建 public class People private String name; private Integer age; }
public class PeopleFactoty public static People newInstance () return new People(); } }
<bean name="people3" class "com.zzf.factory.PeopleFactory" factory-method="newInstance" > </bean>
实例工厂方法创建 public class People private String name; private Integer age; }
public class PeopleFactoty1 public People newInstance () return new People(); } }
<bean name="peopleFactoty1" class "com.zzf.factory.PeopleFactoty1" > </bean> <bean name="people3" factory-bean="peopleFactoty1" factory-method="newInstance" > </bean>
源码查看 1.实例化容器
public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); People people = applicationContext.getBean(People.class); }
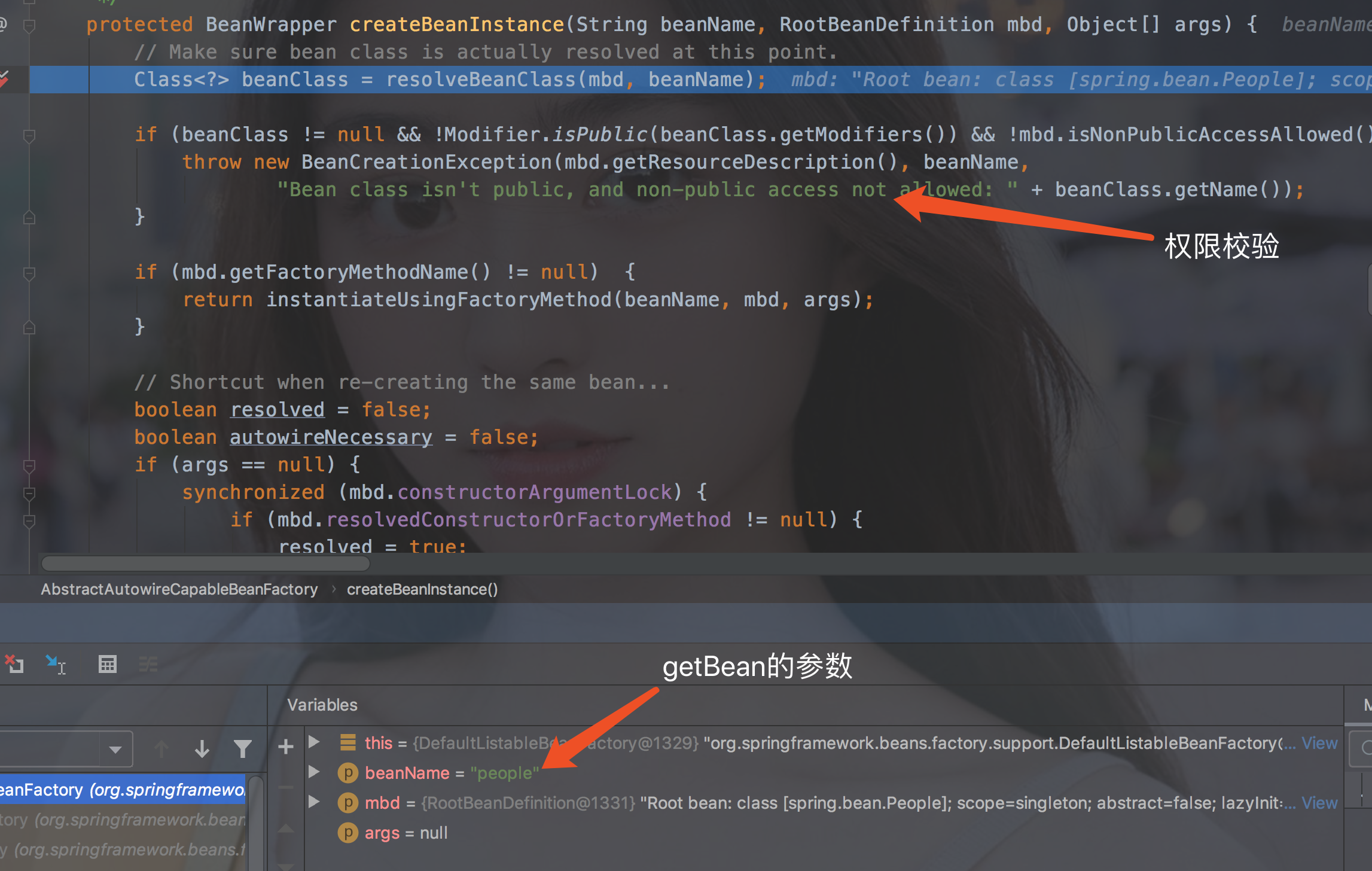
2.org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance (String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName()); } if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null ) { return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args); } boolean resolved = false ; boolean autowireNecessary = false ; if (args == null ) { synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) { if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null ) { resolved = true ; autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved; } } } if (resolved) { if (autowireNecessary) { return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null , null ); } else { return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); } } Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName); if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR || mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) { return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args); } return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); }